In the context of search engines, keywords are terms or phrases that users enter into the search bar to find relevant information on the internet. Search engines use algorithms to match with content available on the web and provide users with relevant search results .


Types
1. Market segment :
These are generic words associated with a specific brand or industry. They target audiences searching for general information, though they can be more specific for niche marketing needs. For example, someone looking to buy shoes for running might search for the general phrase “running shoes” rather than a more specific brand.
2.Customer-defining :
These are intended for a specific category of customers. For example, you might consider the age of your target audience while using these keywords. You can then research their gender, occupation and place of residence in order to target a specific group for advertising. Your customer-defining keywords can address your target audience. If you deal with sportswear products, for instance, a customer-defining keyword to use could be “adult sports enthusiast.” Try to find customer-defining keywords that reflect your brand’s target market demographics.
3.Product-defining :
These describe and explain a product. Customers use product-defining keywords for particular search results, such as specific items. Your brand needs to use product-defining keywords to outline the business’s exact products or services. Buyers search for product-defining keywords when they are at the initial stage of making a purchase.
The best way to use these keywords is by first analyzing your product list and then coming up with a thorough explanation of every product on your list. After that, check the descriptions of your products and select at least two relevant keywords. Use these keywords as your product-defining keywords.
4. Product :
Product keywords that relate to specific brands’ offerings. These keywords are phrases or terms that directly refer to a company’s services or products. Every brand needs to identify product keywords for all its services and products to help its existing and prospective clients find its products via search. If you search for a word such as “copier,” for example, you will most likely get results from a reputable brand. Whatever phrase you type, you will get results from brands that offer those products or services in the industry.
The sports industry, for another example, usually leverages product keywords since companies in this industry link to important sporting events and sportspersons. Someone searching for a prominent person is likely to come across a wide array of products from their sponsor on the first search page .
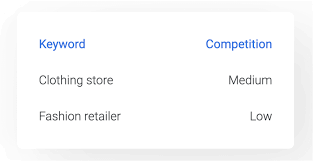
5. Competitor :
These are the keywords that your competitor uses in their marketing strategy to get high search engine rankings. research to uncover the competitor keywords other businesses are using to generate traffic to their websites. Identifying the right competitor helps you understand the specific keywords that are working for your competitors. It further gives you opportunities to draft new content, ultimately boosting your brand’s search engine rankings.
6. Long-tail :
These are usually the longest search keywords, targeting a specific audience or topic. These keywords have low-competing keywords. limited search traffic, making it easier to rank them. Since long-tail keywords are more specific than other keywords, they may have higher conversion rates . A good example might be “best running shoes for injured knees.”
7. Short-tail :
These are also known as generic keywords. The popular, broad search keywords lead to tons of search traffic. This type of keyword comprises less than two words. Furthermore, they rank competitively compared to most keywords. Short-tail are brief and contain one or two phrases. A good example of may be “running shoes.”
8. Mid-tail :
These keywords fall between short-tail and long-tail keywords. Although mid-tail have a relatively more minor traffic volume, they have higher conversion rates and little competition .
9.Intent targeting :
These keywords match the intention of the user while they are searching for a particular phrase. . Marketers can use it to conduct intent-driven marketing. help marketers drive more traffic to their websites, generate more leads, and attract better prospective customers.
10. LSI :
Latent Semantic Indexing (LSI) are conceptual phrases that search engines use to understand a website’s content. For instance, you could write an article about “The Benefits of Eating Eggs.” From the topic, you are writing for an audience that wants to know more about the specific benefits of eating eggs. However, you might forget to mention the phrase ” food” somewhere in your article. Many search engines will still be able to identify and rank your article as a food-related article.
11. Phrase match :
These look for precise matches within a search engine’s search parameter to start an ad. For example, you may search for a site with content such as “dentists who install dental crowns.” Some ads might pop up showing you dental products. These ads are a result of a phrasal match which usually happens in the background. Phrase match usually contains multiple variations to help account for synonyms, misspellings, paraphrases, and implied terms.
12. Exact match :
Exact match are most similar to short-tail keywords. Marketers usually use these keywords to target advertisers whose adverts open up when an internet user searches for a specific phrase on a search engine. search engines use them to target specific audiences with particular ads. Your brand can use these keywords to target people who search for particular terms. Ultimately, these increase your chances of getting conversion.
13.Negative :
These are the opposite of exact match keywords. They prevent ads from popping up once the user searches for a particular term, usually referred to as negative matches. Some search engines consider words like “free” as negative keywords. This means if a user performs a search using this negative word, they might not see certain business results.
14. Related vertical :
These usually offer a more detailed perspective into your business’ content. Let’s say you have a firm that specializes in selling computer hardware, for example. “Computer hardware dealer” could be a horizontal keyword in this context. in this case, might be something like “selling printers” or “RAM for sale.”
15. Locational :
These cover anything that relates to a specific location. Locational keywords are instrumental for locational-based businesses. They might be something like “towing services North Carolina.” Locational keywords can include words or phrases that aim to show ads that have businesses near the person who is searching. In this case, might be such as “towing firm near me.”
16. Long-term evergreen :
that remain relevant indefinitely. While search volume might fluctuate, it won’t affect these keywords. Long-term evergreen keywords remain relevant months and even years after publishing because people will search for content related to these keywords for a long time.
17. Informational :
Informational are keywords that clients use while searching for general information about a particular topic, product, or service. Buyers usually use in the awareness stage of the buying process. Buyers are aware they want a specific product or to solve a particular problem. Thus they need relevant information before they make a purchasing decision. One excellent example might be “what are the best fishing rods?”
18. Navigational :
These are also referred to as “go” keywords. People use these when they want to navigate to a specific brand’s website. People using these keywords already know why they need to buy a product and where they will get those products. Thus, they use specific buying keywords to find the right place to buy what they want. For example, a user might enter the navigational keywords “[brand] running shoes,” using the specific name of the brand of shoe they want to buy.
In this case, the person searching for wants running shoes, and they have decided to get them from a particular company. They are using to navigate to a site that will help them find exactly what they need.
19. Transactional :
Transactional are also referred to as “do” . These are the keywords buyers use when they have already decided to purchase a particular product or service. Buyers use transactional key at the conversation stage of the purchasing process. For example, a user might search “buy running shoes online” when they are ready to make a purchase.
Benefits’ of keywords
- Content Relevance:
- Emphasize the significance of creating high-quality, relevant content that aligns with user intent.
- Discuss how content that addresses users’ needs and interests naturally incorporates terms and phrases relevant to their queries.
- Semantic SEO:
- Explore the concept of semantic SEO, where search engines understand the context and meaning behind words, enabling better content matching.
- Highlight the importance of using language naturally and contextually, allowing search engines to recognize the overall theme and relevance of your content.
- User Intent:
- Emphasize understanding user intent when creating content. When you provide valuable information that aligns with what users are searching for, search engines are more likely to direct traffic to your site.
- Explain that focusing on user intent naturally leads to the integration of terms and phrases that users commonly use.
- Topic Clusters:
- Discuss the concept of organizing content into topic clusters, where a pillar page serves as a comprehensive resource on a broad topic, and cluster content delves into specific aspects.
- Explain how this approach naturally incorporates a variety of related terms, creating a more comprehensive and contextually rich content structure.
- Quality Backlinks:
- Talk about the importance of building high-quality backlinks from reputable sources.
- Emphasize that well-crafted content naturally attracts backlinks, contributing to your website’s authority and visibility in search engine results.
- User Experience:
- Highlight the role of a positive user experience in attracting and retaining visitors.
- Explain that user-friendly websites, with clear navigation and valuable content, tend to perform better in search engine rankings.
- Social Media Engagement:
- Discuss the impact of social media in driving traffic to your website.
- Emphasize that when people share and engage with your content on social platforms, it can indirectly contribute to increased visibility in search engine results.

Add a Comment